The Ultimate Guide to STIR/SHAKEN
As technology progresses, a lot of things that seemed impossible earlier are now possible. VoIP was one such drastic jump in terms of capabilities and opened up a world of possibilities for communications.
Robocalling is one of the capabilities that VoIP unlocked. While automated calls did exist earlier as well, those were limited in function.
However, as new technology appears, so do scams made possible by the misuse of the same technology. Robocalling is no exception.
T-Mobile’s reported almost half a billion scam robocalls are made each week. The result of these scams? A reported loss of $30 Billion for users just in America.
Robocalling when combined with ID spoofing turns into a very effective scam. The FCC is clearly not happy about this and has taken steps to prevent this.
First among these steps, the FCC has mandated telecom players to implement the STIR/SHAKEN framework to combat malicious robocalling and ID spoofing.
But what is the STIR/SHAKEN framework? Let's find out!
What is STIR/ SHAKEN?
STIR/SHAKEN or SHAKEN/STIR is a set of technological protocols set in place to combat ID spoofing over the public telephone network.
When implemented, the STIR/SHAKEN protocol works together to ensure the end users receiving calls are alerted if the call is malicious and with a spoofed identity.
In a study conducted by Transaction Network Services, it was concluded that informing the end user about the authenticity of the call had the highest positive impact on averting robocalling and identity spoofing scams.
Now you know what STIR/SHAKEN is and what it does. We can now dive in deeper and understand its two components.
What is STIR?
Secure Telephone Identity Revisited, commonly abbreviated as STIR, is a protocol of RFC standards documents issued by the working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force.
The protocol works by adding a certificate of identity issued to the caller along with the SIP information at the point of origination.
The certificate can be verified by the terminating caller using the same protocol to authenticate the identity of the caller and inform the end user of the same.
With that out of the way, let's understand what SHAKEN is!
What is SHAKEN?
Signature-based Handling of Asserted information using toKEN, commonly termed SHAKEN, is a set of guidelines for non-VoIP-based systems pertaining to how to deal with calls that have incorrect or missing STIR information.
The STIR protocol is useful only for the VoIP ecosystem. However, a large portion of the telephony network still operates in the non-VoIP ecosystem.
The SIP Forum and Alliance of Telecommunications Industry Solutions jointly developed the SHAKEN protocol. This was to allow for IETF’s STIR standard to be implemented within the legacy telephony networks as well.
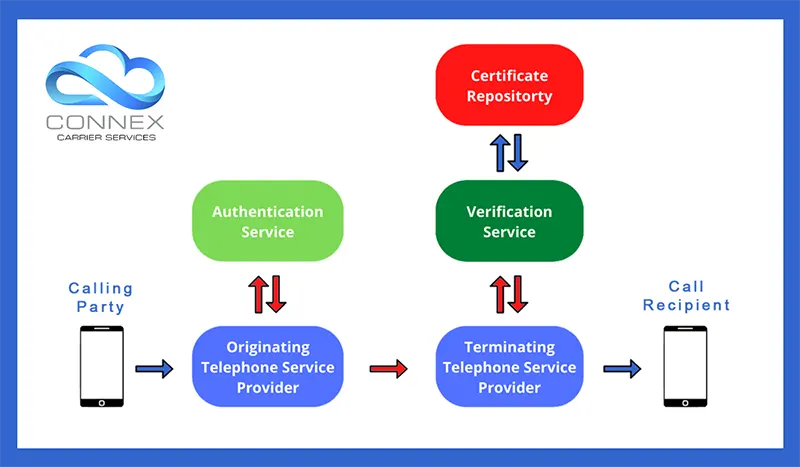
Thus, the SHAKEN protocol allows for authentication and handling of calls within the legacy telephony network.
Together, STIR/SHAKEN covers the entire telephony network, legacy and VoIP and makes sure spoofed identities are kept in check and the end users are informed about the same.
Considering the number of telecom carriers involved in putting a call through, it is not possible to be absolute about the caller identity. Thus, the STIR/SHAKEN protocol issues a level of attestation. Let us learn more about it.
Attestation Levels
Telecom networks are huge and complex. There are multiple carriers involved in handling a single call. This necessitates the use of attestation levels.

The level of attestation represents the confidence of a carrier in attesting that the caller’s identity has not been spoofed.
Accordingly, we have three levels of attestation. They are as follows:
Full Attestation (A) -
Level A attestation by the carrier means:
- The carrier has authenticated the origin of the call.
- The carrier has authenticated the calling party.
- The carrier has authenticated that the calling party is authorized to use the calling number.
An example of this would be a call originating from a regular subscriber of a voice service with a carrier.
Partial Attestation (B) -
Level B attestation by the carrier means:
- The carrier has authenticated the origin of the call.
- The carrier has authenticated the calling party.
- The carrier has not authenticated whether the calling party is authorized to use the calling number or not.
An example of this would be a call originating from behind a PBX of an organization.
Gateway Attestation (C)
Level C attestation by the carrier means:
i) The carrier has authenticated the source from where it received the call. ii) The carrier has not authenticated the calling party. iii) The carrier has not authenticated whether the calling party is authorized to use the calling number or not.
With the basics of STIR/SHAKEN now explained, we can move on and understand how the system works.
How does STIR/SHAKEN work?
The STIR/SHAKEN framework adds a few additional steps to a regular calling process to eliminate the risks of caller ID spoofing.
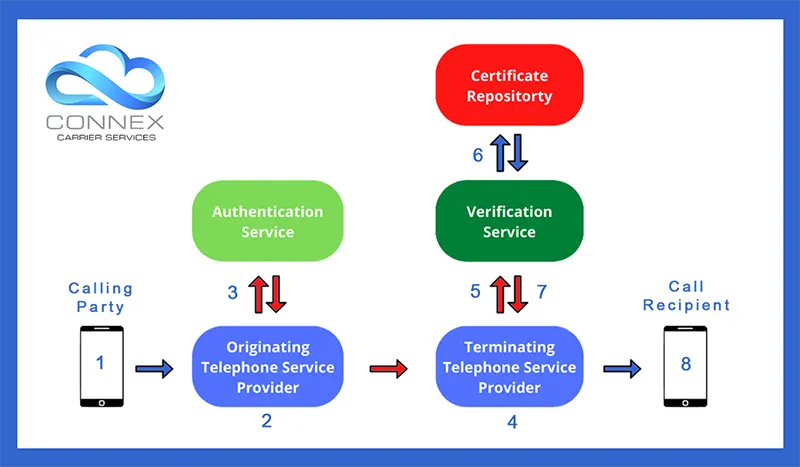
There are 8 steps involved in the working of the STIR/SHAKEN framework. These are as follows:
1. Call Originates
When a caller dials in a number or places a call to a contact, a SIP invite is received by the originating telephone service provider.
2. Attestation
The originating telephone service provider is required to check and verify the identity, source and authorization for using the calling number by the calling party.
Accordingly, the originating telephone service provider determines an attestation level to the originating call.
3. Signing
Usually, a third-party authentication service is used by the originating telephone service provider to add all the necessary information and attestation level to the SIP header associated with the call The SIP header contains the following information:
- Calling number
- Called number(s)
- Current timestamp
- Attestation level
- Origination identifier
4. Transfer to Terminating Telephone Service Provider
The SIP invite along with the SIP header containing all the necessary information is then transferred to the destination telephone service provider, more commonly known as the terminating telephone service provider.
5. Transfer to Verification Service Provider
The terminating telephone service provider then forwards the SIP header to a third-party verification service.
6. Verification
The verification service obtains the SIP header and examines it. Based on the information provided, it procures the digital certificate of the originating telephone service provider from the public certificate repository.
Once everything needed to verify a call has been procured, a multi-step verification process commences.
- The SIP Identity header is base64 URL decoded and the details are compared to the SIP INVITE message.
- The public key of the certificate is used to verify the SIP Identity header signature.
- The certificate chain of trust is verified.
If the call passes all the verification steps, it is established that the call has not been spoofed. After verification is complete, the results are forwarded to the terminating telephone service provider.
7. Verification reported to Terminating Telephone Service Provider
The verification service reports in detail the verification result to the terminating telephone service provider.
8. Final Assessment
Once the results of the verification are known by the terminating telephone service provider, it can resort to one of the following options depending upon the verification results:
i) If the verification has been successful, it completes the call. ii) If the verification is partially successful, it completes the call but issues caution to the end user. iii) If the verification fails, it may opt to reject the call request.
Now you know how STIR/SHAKEN works in practice. However, there are some impacts of implementing STIR/SHAKEN, let's learn about those.
Impacts of Implementing STIR/SHAKEN
You may have already noticed how complicated the entire process is. In practice, implementing the STIR/SHAKEN framework results in noticeable downsides. These are:
1. Added Complexity
If you consider a normal SIP process, it involves 4 steps. With STIR/SHAKEN implemented, the number of steps required doubles.
Not only do the steps double but these steps are complex to perform. This added complexity further results in other downsides.
2. Increased Latency
Double the number of steps needed and add more complexities to any function and it will result in more time being required to execute that process.
STIR/SHAKEN is necessary to eliminate the risks of malicious robocalls and spoofed identities. However, it slows down the entire telephony network.
3. Added Costs
If you consider the process, you need a certificate issuer, third-party authenticator and verification services. These add to the primary costs.
Additionally, as the entire process slows down the network, you incur the opportunity costs due to lowered throughput.
4. Additional Failure Points
Not only does the STIR/SHAKEN framework introduce additional failure points in the process but most of them are external.
If either of the authentication, verification or public certificate repository go down, you won’t be able to get calls through.
However, implementing STRI/SHAKEN is no longer optional. The FCC requires all telecom operators and carriers to use the system by default from late 2021.
I know what you’re wondering. Shouldn't there be a way to minimize the impact of these downsides? Yes, there is one solution that ConnexCS has come up with. Let's check it!
Comparing ConnexCS STIR/SHAKEN with STIR/SHAKEN 3rd Party Signing.
ConnexCS has been offering the STIR/SHAKEN functionality for some time now. While implementing it, we realized the impacts our customers may face along with it.
Thus, to lessen the impact of implementing STIR/SHAKEN on our customer’s businesses, ConnexCS came up with a solution.
So what is the solution you ask? All of our products come integrated with signing and verification functionality. Both functions runs in line with the calling function.
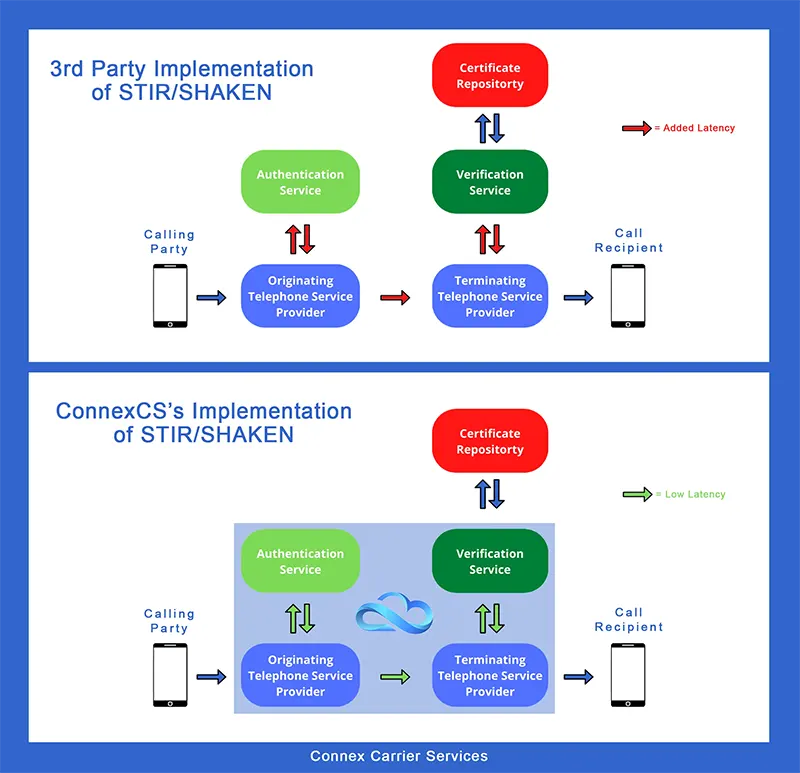
You don’t have to rely on a third-party authenticator for complying with the STIR/SHAKEN protocol.
Let's talk numbers! Integrating the authentication function in our products lessens the latency and complexity of operations by up to 44%.
Moreover, you eliminate a big failure point by having the authentication service integrated into your carrier services.
While you will still be dependent on third-party verification and public certificate repository, you’re making significant gains through ConnexCS’s services.
Concluding
It's not just the American telecom market that is plagued with malicious robocalls and identity spoof scams. These scams run rampant all over the world.
The FCC may be the first national agency to make STIR/SHAKEN mandatory. However, we’re positive that the EU and other nations will follow suit.
Thus, implementing STIR/SHAKEN at the earliest is the need of the hour. If you choose to do so with ConnexCS, you’ll be benefiting from additional savings too.
Want to know how to get started, look at our other article here.
























































































































