Understanding Network Address Translation (NAT) - A Beginner's Guide
We can now sit in the comfort of our homes and make calls across the world with a click. Video calling has become quite seamless too and VR lets us attend concerts and events virtually.
I am at home as I write this article, almost 7500 km away from our head office. I'm constantly in contact with all my colleagues spread across the world. We talk, brainstorm, solve problems and create value together and do all of it remotely.
For what seems to be a wonderful performance on stage by the internet, a lot goes on backstage to make all of this possible. One important thing that makes all of this possible is Network Address Translation.
You may have heard about this or seen it as an option while tweaking your router settings. With this article, you’ll understand everything there is to learn about NAT.
Let’s begin now, shall we?
What is Network Address Translation?
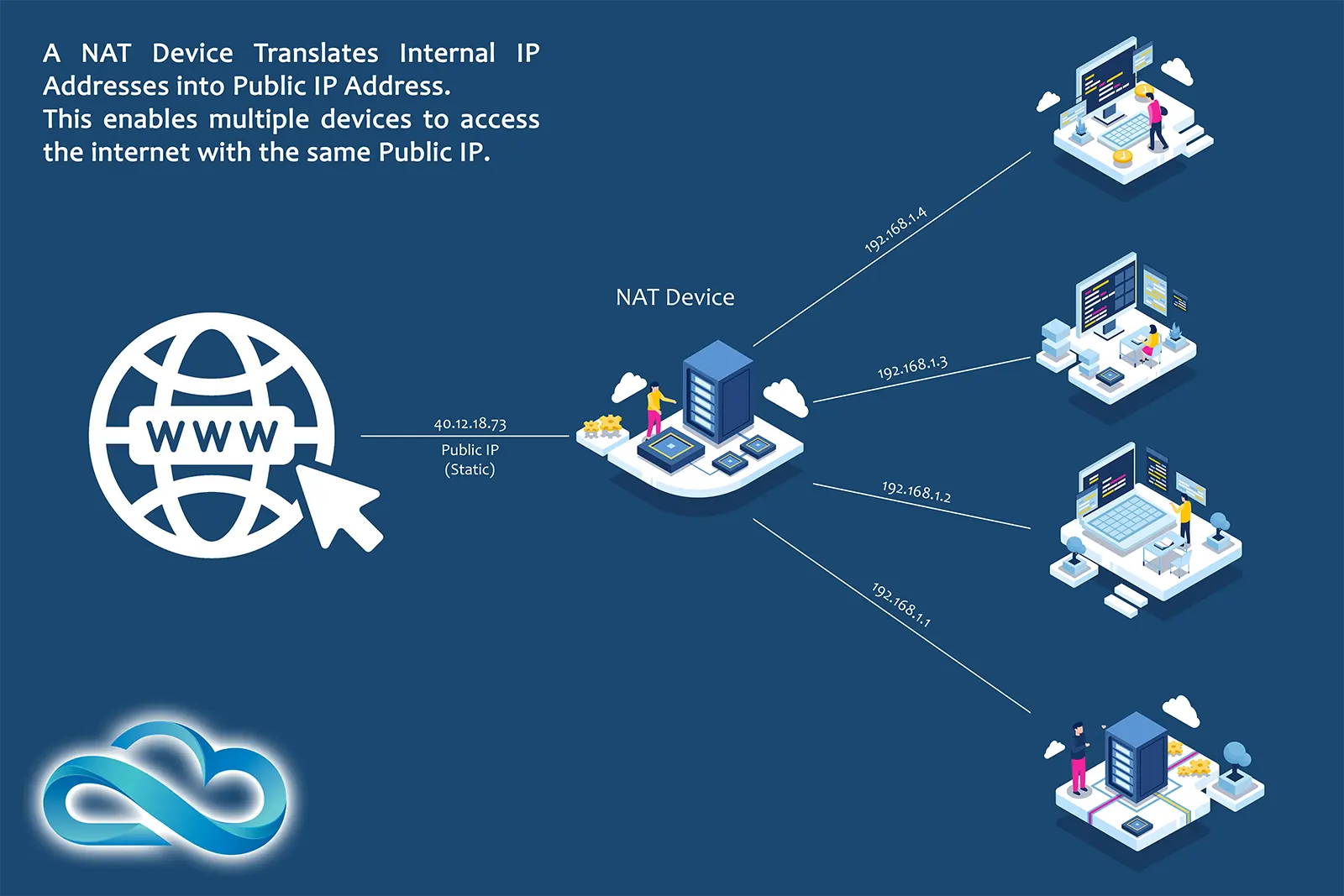
Network Address Translation (NAT) is like an intermediary between a private network and the internet. It allows multiple devices connected to it to connect to the internet using the same public IP address.
NAT assigns IP addresses to all the devices connected to it and maintains a record of these IP addresses. When a connected device wants to access the internet, NAT translates its assigned IP address to the router's public address.
When a response is received from the internet, NAT looks up the IP records and sends the data back to the correct device.
This way, multiple devices can use the internet while appearing to have a unique IP address. This makes the network more secure and efficient.
Thus, NAT enables an entire private network to access the internet using a single public IP address. This eliminates the need for a unique IP address for every device and thus, the limited IPv4 addresses are conserved.
Now that we know what NAT is, let’s find out why is it so necessary!
Why Is NAT Necessary?
The internet works similarly to telephone service. If you want to find out something from someone, you have to call the particular person and ask for the information. To do so using a telephone, you need to dial that person’s phone number and talk to them.
On the internet, devices talk to one another and information is exchanged between them. Similar to phone numbers, the internet has specific addresses for all devices connected to it. These addresses are known as Internet Protocol (IP) addresses.
At present, we’re using the IPv4 standard for internet communication. There are a total of 4.294 Billion IPv4 addresses available for use. In contrast, according to the latest reports, there are about 14.4 Billion devices connected to the internet.
So how are 14.4 billion devices connected to the internet when only 4.29 Billion IPv4 addresses are available? This was made possible using NAT.
NAT helps to extend the limited availability of IPv4 addresses. It allows organizations to use a single public IP address to represent many private IP addresses on a local network.
In a NAT environment, the local network uses private IP addresses that are not globally unique. When a device on the local network wants to access the internet, it sends a request through the NAT device.
The NAT device translates the private IP address of the device into the public IP address of the organization, which is then used to access the internet.
The response from the internet is then translated back into the private IP address of the device by the NAT device. This allows organizations to use a single public IP address to represent multiple private IP addresses on a local network.
As a result, fewer public IP addresses are needed to connect multiple devices to the internet, which helps to conserve globally unique IPv4 addresses.
Now you know why NAT is Necessary. There are additional reasons that make NAT important too. Let’s find them out!
Why is NAT Important?
We’ve just covered the primary reason why NAT is critical for internet communication. However, several other reasons make Network Address Translation (NAT) so important. These are as below:
Address Conservation
The IPv4 address space is limited, and NAT helps to conserve globally unique IPv4 addresses. NAT allows organizations to use a single public IP address to represent many private IP addresses on a local network.
This helps to extend the life of IPv4 addresses, as fewer public IP addresses are needed to connect multiple devices to the internet.
Network Security

NAT provides an added layer of security for devices on a local network. The internal IP addresses are hidden behind a public IP address.
This helps to protect the devices from being directly targeted by malicious actors on the internet. Additionally, NAT can prevent unauthorized access to resources on the internal network by external devices.
IP Address Conflict Resolution

NAT helps to reduce the risk of IP address conflicts on a network. The internal IP addresses are hidden behind a public IP address.
This allows organizations to use the same private IP addresses on multiple internal networks, even if they are connected to the internet.
As there is a dedicated device monitoring and managing the traffic, all inbound and outbound connections are routed correctly.
Scalability

NAT enables organizations to add and remove devices from a network without having to worry about IP address conflicts or changing IP addresses for existing devices.
As devices are added or removed, the NAT mapping table is updated dynamically, allowing the network to scale smoothly and without disruption.
Quality of Service (QoS)

NAT allows administrators to prioritize and manage network traffic based on the type of data being transmitted. For example, administrators can prioritize voice and video traffic over other types of data traffic.
This ensures that these types of real-time communications are not impacted by network congestion. Moreover, one can manage and allocate network bandwidth and access to devices as per requirements.
With that, we’ve covered all the reasons why NAT is important. Let’s leave no stones unturned and proceed to understand NAT Implementation.
How to Implement NAT on a Router or Firewall

I'm sure you’re already convinced of the importance of NAT by now. So the obvious question in your mind now must be ‘How do I implement NAT?’ Let me answer that.
Network Address Translation (NAT) can be implemented using a router or firewall as follows:
Configuring the Router or Firewall
NAT can be implemented on a router or firewall by configuring the device to perform NAT functions. This typically involves specifying the public IP address to be used for NAT, and the private IP address range to be translated.
Another thing that needs to be specified is the type of NAT to be performed (e.g. static NAT, dynamic NAT, or port address translation).
Mapping Private to Public IP Addresses
The router or firewall maps private IP addresses to public IP addresses. This will allow devices on the private network to communicate with devices on the public network.
This is done by translating the source IP address of packets from a private IP address to a public IP address, and vice versa for packets received from the public network.
Performing NAT Functions
The router or firewall performs NAT functions by intercepting packets between the private and public networks and translating the source IP addresses of the packets.
NAT can be performed using static NAT, dynamic NAT, or port address translation, depending on the specific requirements of the network.
Maintaining NAT Tables
The router or firewall maintains NAT tables to track the mapping of private to public IP addresses. This allows it to correctly translate the IP addresses of packets as they are forwarded between private and public networks.
Filtering Packets
In addition to performing NAT functions, the router or firewall can also be configured to filter packets based on their source and destination IP addresses, ports, and other parameters.
This allows the router or firewall to provide additional security and control over the network by blocking unwanted or malicious traffic.
How can NAT be used for Network Security?

NAT can provide some security benefits in a network environment. Here are a few common security applications of NAT:
Hiding Internal Network Information
NAT can hide the internal network IP addresses from external sources by translating them to a single public IP address. This can make it more difficult for external sources to target specific internal devices.
Provide Basic Firewall Functionality
NAT can act as a basic firewall by filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on the source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols. This can prevent unauthorized access to internal network resources.
Limit Access to Specific Resources
NAT can be configured to allow only specific types of traffic, such as HTTP or HTTPS, to access specific resources, such as a web server.
Restrict Incoming Traffic
NAT can restrict incoming traffic from the Internet to the internal network, making it more difficult for external sources to initiate a connection to internal devices.
Masquerade Multiple Internal Devices
NAT can masquerade multiple internal devices as a single public IP address, making it more difficult for external sources to identify specific internal devices.
It's important to note that NAT is not a replacement for a full-fledged firewall. It should not be relied upon as the sole security measure in any network environment.
Additionally, NAT can introduce potential security risks, such as address spoofing and hairpinning. So it's important to understand its limitations and to use it in conjunction with other security measures.
Finishing Up
To say NAT is important for the operations of the Internet of the present would be an understatement. Everything you’ve learnt through this article should be enough to reinforce this.
The eventual roll-out and adoption of the IPv6 standard will disrupt the usage of NAT. However, NAT is versatile enough that it will still find a place for itself in the future of the Internet.
Tell me, would you like to learn more about NAT?
























































































































