Far-End NAT Traversal - An In-Depth Guide
The Internet runs on a varying set of underlying technologies that make some amazing things possible. NAT is one such technology that enables every device to access the internet without needing a dedicated IPv4 address.
While this is a big convenience that NAT offers us, it creates a few hindrances of its own. One such hindrance is how NAT makes real-time communication difficult.
Network address translation can create difficulty in establishing a direct line of bidirectional communication between two endpoints. Thankfully, this can be overcome.
The technology that enables this is known as Far-End NAT Traversal. If you’re wondering what it is and how it works, you’re not alone. We’ll be answering all such questions and more in this article.
Let’s get started then, shall we?
What is Far-End NAT Traversal?
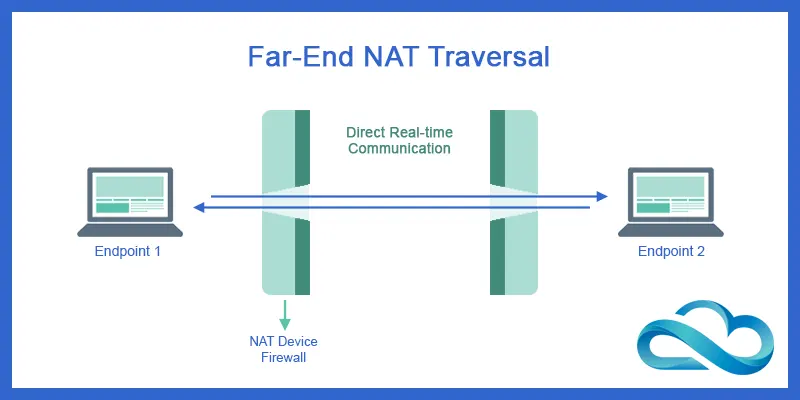
Far-end NAT traversal is a method that allows two devices, both behind a firewall or network address translator (NAT), to communicate with each other directly.
NATs are used to map private IP addresses to public IP addresses, but this makes it difficult for the two devices to connect directly.
Far-end NAT traversal solves this problem by using a relay server to help the devices find and connect with each other, bypassing the NATs. This results in a faster and more stable connection between the two devices.
Far-End NAT Traversal is crucial for real-time applications as it ensures that these applications work as intended, regardless of the presence of NAT.
Now that you know what Far-End NAT Traversal is, let’s find out why exactly it is necessary!
Why is Far-End NAT Traversal Necessary?
Knowing what technology does is just one part of the story. Knowing why it was necessary, to begin with, will help you understand any technology better. Far-end NAT traversal is necessary for the following reasons:
To Enable Communication Between Two Devices Behind Different NATs
Far-end NAT traversal enables two devices, both located behind separate NATs, to communicate with each other directly. Without far-end NAT traversal, the NATs would block the communication between the two devices.
To Bypass The NATs
Far-end NAT traversal bypasses the NATs, allowing the two devices to communicate directly with each other, without going through the NATs.
To Improve The Performance and Reliability of Communication
By establishing a direct connection between the two devices, far-end NAT traversal improves the performance and reliability of the communication, as the devices can communicate directly, without the need for a relay server.
To Reduce the Load on the Relay Server
By bypassing the relay server and establishing a direct connection between the two devices, far-end NAT traversal reduces the load on the relay server, improving its performance and reliability.
Consider a scenario where Alice and Bob both want to make a voice call to each other using a VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) application. Both Alice and Bob are located behind NATs, so they cannot communicate directly with each other.
If they try to make a call without far-end NAT traversal, the call will fail because the NATs will block the connection.
With far-end NAT traversal, the two users can connect to a relay server, which will help them discover each other's private IP addresses.
Once the private IP addresses are discovered, the users can establish a direct connection and make a call without going through the relay server.
With that, you know what Far-End NAT Traversal is necessary. The next question I’ll answer is how it works.
How Does Far-End NAT Traversal Work?
Far-end NAT traversal works by bypassing the NATs and allowing the two devices to communicate directly with each other. The process can be broken down into the following steps:
Device discovery

The first step in far-end NAT traversal is discovering the other device's private IP address. This is usually done using a relay server, which acts as a middleman between the two devices.
The relay server helps the devices to identify each other's private IP addresses, which are required for the direct connection to be established.
Connection setup

Once the private IP addresses have been discovered, the devices can establish a direct connection with each other. They exchange information such as port numbers, which are required for the direct connection to be established.
The port numbers are used to distinguish between different connections and are used to direct incoming packets to the correct application.
NAT traversal
To bypass the NATs and establish a direct connection, the devices use a technique called NAT traversal. This involves sending packets to each other in a specific way.
It enables the NATs to recognize the connection as legitimate and allow the packets to pass through.
The endpoints send special packets called "NAT keepalive" packets to each other. These packets help in maintaining the connection between the endpoints and ensure that the NAT device does not time out the connection.
Several NAT traversal techniques can be used, including hole punching, using a relay server to send messages between the devices, and using UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) to configure the NATs dynamically.
Communication

With the direct connection established, the two devices can communicate with each other directly, without going through the relay server.
This results in a faster and more reliable connection, as there is no longer any need for the relay server to process and relay messages between the devices.
Now you know a fair bit about Far-End NAT Traversal. Let’s check what benefits it offers.
Benefits of Far-End NAT Traversal
While enabling direct real-time communication is the primary benefit, Far-End NAT Traversal has more to offer. Additional benefits that Far-End NAT Traversal offers are as follows:
Improved Performance

By bypassing the NATs and establishing a direct connection between two devices, far-end NAT traversal significantly improves the performance of communication.
The direct connection eliminates the need for a relay server to process and relay messages between the devices, resulting in faster and more reliable communication.
Reduced Latency
With the direct connection established, there is no longer any need for the relay server to process and relay messages between the devices.
This reduces the latency of the connection, as messages are sent directly from one device to the other, without the need for intermediate processing.
Increased Reliability
Far-end NAT traversal reduces the dependence on the relay server, making communication between two devices more reliable.
The direct connection eliminates the possibility of messages being lost or delayed due to issues with the relay server.
Increased Scalability

By eliminating the need for a relay server, far-end NAT traversal allows for more devices to communicate directly with each other. This increases the scalability of communication networks.
The direct connections between devices reduce the load on the relay server, allowing it to handle more connections.
Better Network Utilization
Far-end NAT traversal allows for direct communication between devices behind separate NATs, reducing the need for a relay server.
This increases the utilization of network resources and reduces the load on the relay server, making communication more efficient.
Improved Quality of Service (QoS)

With the direct connection established, communication between devices is not dependent on the performance of the relay server.
This results in a more stable connection, reducing the chances of connection drops or delays, and providing better QoS for users.
Better Audio and Video Quality

Far-end NAT traversal is also beneficial for audio and video communication, as it enables direct communication between devices.
This results in a higher-quality audio and video experience, with reduced latency and improved reliability. All of which are crucial for any form of real-time communication.
Cost Savings
By reducing the need for a relay server, far-end NAT traversal can help to reduce the costs associated with the communication.
The direct connection eliminates the need for intermediate processing and reduces the load on the relay server, reducing the costs of network infrastructure and maintenance.
Wherever there are benefits, there are also some drawbacks. Let’s take a look at the drawbacks of Far-End NAT Traversal.
Drawbacks of Far-End NAT Traversal
While Far-End NAT Traversal is an amazing piece of technology, it does have its fair share of drawbacks. Enabling real-time communication flawlessly comes at a cost.
Added Complexity
Far-end NAT traversal can be complex and difficult to set up, especially for those who are not familiar with network configurations. It requires a deep understanding of NAT and firewall configurations, port forwarding, and other related topics.
Limited Compatibility
Not all applications or protocols are compatible with far-end NAT traversal. Some applications may require specific ports to be open, which may not be possible if the NAT firewall is strict.
Security Risks

Far-end NAT traversal can pose security risks if not configured properly. NAT firewalls are designed to protect networks from unauthorized access, and opening ports to allow far-end NAT traversal can potentially expose networks to security threats.
Increased Latency
NAT firewall devices can add latency to the connection, causing a decrease in the overall performance of the connection. This can be especially problematic for real-time applications, such as video conferencing, where even small amounts of latency can cause significant degradation of the user experience.
Bandwidth Constraints
NAT firewalls may have restrictions on the amount of bandwidth that can be used for a single connection, which can limit the performance of the connection.
With that, we hope you’ve gained a thorough understanding of Far-End NAT Traversal. Let’s top off your efforts and also understand how Far-End NAT Traversal can be implemented.
Implementation of Far-End NAT Traversal
Far-end NAT traversal can be implemented in several ways, including the following:
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP)
UPnP is a widely used protocol that allows devices to automatically discover and configure port forwarding on the NAT.
UPnP is commonly used to implement far-end NAT traversal, as it provides a simple and automated way to configure port forwarding on the NAT.
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is another way to implement far-end NAT traversal. Port forwarding involves manually configuring the NAT to forward incoming traffic to a specific device behind the NAT.
This allows the device to receive incoming traffic from the internet and communicate directly with other devices.
Application-Level Gateways (ALGs)
ALGs are gateways that are integrated into the NAT and are specifically designed to support specific applications.
ALGs can be used to implement far-end NAT traversal by automatically modifying NAT translations for specific applications, allowing them to bypass the NAT.
Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN) and Traversal Using Relays around NAT (TURN)
STUN and TURN are protocols used to traverse NATs. STUN is used to determine the public IP address of a device behind a NAT, while TURN is used as a relay server to forward messages between devices.
Far-end NAT traversal can be implemented using STUN and TURN by using the STUN server to determine the public IP address of the devices behind the NATs and using the TURN server to relay messages between the devices.
Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE)
ICE provides a standardized and effective way for devices behind NATs to establish a direct connection for real-time communication.
By using STUN and TURN, ICE allows for high-quality, low-latency communication, even in challenging network environments where NATs are present.
Conclusion
Far-End NAT Traversal is a crucial aspect of modern networks that helps in ensuring the proper functioning of real-time applications.
It helps in improving the reliability, security, and performance of these applications. It is implemented using various techniques such as STUN, TURN, and ICE.
While it does have a few drawbacks, overall, what it enables, far outweighs those drawbacks.
What would you like to learn next?
























































































































