What Are VoIP Gateways and How Do They Work? A Comprehensive Guide
Changes can be quite uncomfortable to cope with. Imagine spending a thousand dollars on the latest piece of technology, only for it to become outdated in a few months.
The same problem exists on a bigger scale when it comes to businesses and organizations. They invest heavily in certain technologies necessary to conduct business. When better technology comes along, it gets difficult to upgrade to it.
Not only would it come at a big cost but also introduce a lot of disruption to a firm’s day-to-day functioning. Businesses were left facing the same problem when VoIP came along to replace legacy communication systems.
Thankfully, there was a way businesses could keep using their legacy systems and yet benefit from the advantages VoIP had to offer. All of this was facilitated by VoIP Gateways. In this blog, we will learn every important thing about a VoIP Gateway.
Let’s get started then!
Understanding VoIP Gateways

In the ever-evolving landscape of modern communication, VoIP gateways are ensuring seamless connectivity. They facilitate the transition from traditional telephony to digital voice communication.
Defining VoIP Gateways
A VoIP gateway is a device or software application responsible for the conversion and routing of voice calls between traditional analog phone lines and digital IP networks.
These gateways act as the intermediaries between different communication technologies, allowing voice data to travel across various mediums.
VoIP gateways are a fundamental component of VoIP infrastructure and are designed to handle the intricacies of voice transmission. Thus ensuring that conversations are clear and uninterrupted.
The analog-to-digital transition in terms of communication is still going to take some time. As a result, bridging the gap between traditional and digital communication has become a vital function.
VoIP Gateways enable interoperability by facilitating the seamless exchange of voice data between analog and IP networks. Their global connectivity empowers international communication without any added exorbitant costs.
Cost efficiency is a significant advantage, reducing expenses associated with legacy phone systems. VoIP gateways offer scalability for evolving communication needs and access to advanced features, enhancing productivity.
Flexible, reliable and efficient communication services are the need of the hour for businesses and individuals alike, around the world. VoIP Gateways are playing a central role in delivering upon these expectations.
With the basics covered, let’s move on to the next thing. We shall now learn how VoIP Gateways work!
How Do VoIP Gateways Work?
VoIP gateways serve as essential components in the architecture of VoIP communication systems. Here, we will delve into the technical processes, key components, and functions of VoIP gateways.
1. Analog-to-Digital Conversion
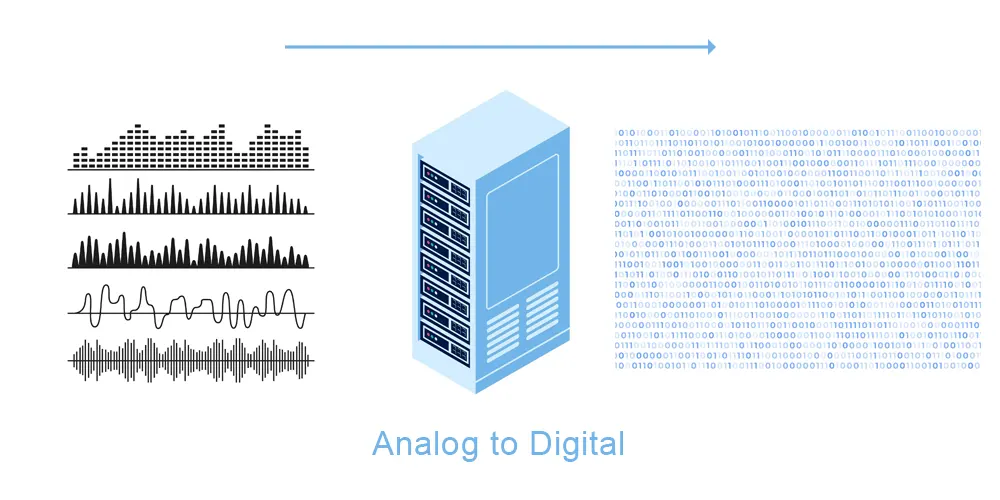
VoIP gateways play a crucial role in converting analog voice signals, as typically found in traditional telephone systems, into digital data packets suitable for transmission over IP networks. This process involves several steps.
Analog Signal Input: The gateway receives incoming analog voice signals from devices like analog phones or fax machines.
Analog-to-Digital Conversion: An Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) samples the analog signal at regular intervals. Then it quantizes the amplitude of the signal, and digitizes it. This produces a stream of digital data that represents the voice signal.
2. Compression and Encoding

After digitization, the voice data may be compressed to optimize bandwidth usage. Common audio codecs, like G.711 or G.729, are used to reduce the size of the data while maintaining reasonable voice quality. Encoding the voice data into a format suitable for IP transmission is part of this process.
3. Packetization

The compressed and encoded voice data is segmented into small data packets. These packets are organized and formatted with relevant header information. The source and destination addresses, sequence numbers, and timestamps are included in the header.
This is crucial for ensuring that packets are transmitted in the correct order and can be reassembled at the destination.
4. Protocol Conversion
Protocol Conversion with VoIP Gateways
VoIP gateways facilitate the transfer of voice packets between different networks. In this process, the gateway may need to convert the protocol used for voice transmission. For instance, it might convert from the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) protocol to SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) for VoIP networks.
Key Components and Functions
1. Interface Ports
VoIP gateways have physical ports to connect to various types of communication networks. These may include analog ports for connecting to traditional analog phones, digital ports for ISDN or T1/E1 lines, and Ethernet ports for connecting to IP networks.
2. Codec and DSPs
Codecs (Coder-Decoder) are responsible for compressing and encoding voice data. Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) may also be present to perform real-time processing tasks, like echo cancellation and noise reduction, to ensure voice quality.
3. Signaling and Control
VoIP gateways manage call setup and teardown, as well as signaling protocols. They communicate with call control servers, handle call routing, and establish connections between different network segments.
4. Quality of Service (QoS) Management
Ensuring a consistent and high-quality voice experience is paramount. VoIP gateways monitor and manage QoS, prioritizing voice traffic to reduce latency and packet loss.
5. Security Measures
Security features, including firewall capabilities and encryption, are often integrated to protect VoIP networks from unauthorized access and eavesdropping.
That should have furthered your knowledge about VoIP Gateways. Let’s double down upon it and learn about the different types of VoIP Gateways!
Types of VoIP Gateways
There are several types of VoIP gateways, each designed for specific purposes in the realm of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) communication. Here's a list and explanation of the different types of VoIP gateways:
1. Analog VoIP Gateways
Analog gateways interface with traditional analog devices, such as analog phones, fax machines, and analog telephone lines (PSTN). They convert analog signals to digital data, making it possible to integrate these devices into VoIP networks.
2. Digital VoIP Gateways
Digital gateways are used to connect digital phone systems, like ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) or E1/T1 lines, to VoIP networks. They convert digital signals into VoIP-compatible data, ensuring the smooth transition of digital voice traffic.
3. SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) Gateways
SIP gateways handle the conversion between traditional telephone systems and SIP-based VoIP networks. They facilitate voice communication over the internet by translating SIP signaling to traditional telephony protocols and vice versa.
4. Media Gateways
Media gateways focus on handling the media aspects of VoIP, including audio, video, and other multimedia content. They often serve in scenarios like video conferencing, multimedia streaming, and interactive communication.
5. Trunking Gateways
Trunking gateways connect multiple lines or channels from a Private Branch Exchange (PBX) to a VoIP network. They ensure the efficient flow of voice traffic from the PBX to VoIP providers.
Thus, trunking gateways are ideal for businesses seeking to leverage VoIP services while retaining their existing PBX infrastructure.
6. Residential Gateways
These gateways are designed for home users, allowing them to connect their traditional telephones to VoIP services. They often come equipped with additional features such as routers, wireless access points, and built-in security.
7. VoIP-to-VoIP Gateways
These gateways facilitate communication between different VoIP networks or service providers. They help bridge the gap between various VoIP protocols and systems, allowing for seamless, cross-network communication.
With the different types of VoIP Gateways covered, we can now move to understanding the different advantages of using them.
Advantages of Using VoIP Gateways
One can come up with a range of advantages for using VoIP Gateways for different scenarios and deployments. Here are the top five general advantages of using VoIP Gateways in telecommunication networks.
1. Cost Savings

VoIP gateways significantly reduce communication costs. They convert analog voice signals into digital data. They allow voice traffic to be transmitted over the Internet, which is often more cost-effective than traditional telephone lines. This leads to savings in long-distance charges and the maintenance of legacy phone systems.
2. Global Connectivity
VoIP gateways enable global communication without the need for expensive international calls. By utilizing the internet for voice transmission, they allow individuals and businesses to connect with others worldwide. Thus, facilitating international collaboration and expanding market reach.
3. Scalability

VoIP gateways offer scalability, allowing businesses to adapt to changing communication needs. VoIP gateways can be easily configured or expanded to accommodate evolving requirements. Thus, preventing the need for costly infrastructure changes and costs associated with friction due to these arising changes.
4. Flexibility and Advanced Features

VoIP gateways support a wide range of advanced communication features. These include call routing, voicemail-to-email, conferencing, and more. This flexibility enhances productivity and enables innovative communication solutions for businesses.
5. Legacy System Integration
Many organizations have invested in legacy telephone systems. VoIP gateways help integrate these systems with VoIP networks. Thus, preserving previous investments and making the transition to modern communication technology smoother.
This allows businesses to adopt VoIP technology gradually while leveraging existing infrastructure.
As a result, VoIP Gateways empower businesses and individuals to reduce costs, expand their reach, and enjoy the benefits of advanced communication features.
VoIP Gateways vs. Routers?
After going through all of this, one might think that routers and VoIP Gateways perform similar functions. Both handle and manage internet traffic, act as bridges between networks and more. But are they the same? If not, what makes them different?
Quite definitely, these are not the same. Here are the main differences between a VoIP Gateway and a Router.
1. Primary Function
VoIP Gateway: A VoIP gateway is primarily designed for the conversion and routing of voice calls between different communication networks. It bridges the gap between traditional analog or digital phone lines and digital IP networks.
Router: A router, on the other hand, is primarily used for data packet routing between different IP networks. It directs data traffic between devices within a network and facilitates the connection to external networks, like the Internet.
2. Data Type Handling
VoIP Gateway: VoIP gateways are focused on handling voice data. They convert analog voice signals to digital data and are optimized for real-time voice transmission.
Router: Routers manage all types of data traffic, including voice data. While they can handle VoIP traffic, they do not specialize in voice processing and may not provide the same quality of service for real-time voice communication.
3. Voice Processing and Codecs
VoIP Gateway: VoIP gateways often incorporate specialized voice processing components, like codecs and Digital Signal Processors, which ensure high-quality voice transmission. They are equipped to compress, encode, and process voice data.
Router: Routers lack dedicated voice processing capabilities. They typically do not have codecs or DSPs designed for real-time voice communication.
4. Call Control and Signaling:
VoIP Gateway: VoIP gateways manage call setup, teardown, and signaling for voice communication. They are responsible for handling protocols like SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) for VoIP networks.
Router: Routers focus on data packet forwarding and do not have the same level of involvement in call control or voice-specific signaling.
5. Voice Quality and Real-Time Communication
VoIP Gateway: VoIP gateways are optimized for voice quality and real-time communication. They prioritize voice traffic to ensure low latency and high-quality voice transmission, making them ideal for voice calls.
Router: Routers are designed to manage data traffic efficiently but may not provide the same level of QoS for real-time communication. While they can handle VoIP traffic, they might not deliver the same voice quality or reliability as VoIP gateways.
With that, we’ve covered everything important that you need to know about VoIP Gateways, Let’s wrap things up!
Ending Notes
People have a difficult time adjusting to changes. Especially when those changes might make previous big investments redundant. The solution? Deliver the change with minimal actual change!
VoIP Gateways are one such solution. With these, you won’t need to discard the desk phones, phone lines, on-premise PBX systems and other investments.
A VoIP Gateway will let you benefit from the advantages of VoIP while keeping legacy systems as is. Thus, you can make the most out of your earlier investments while not missing out on any cost savings and features.
























































































































