Discover the Different Types of NAT: An Essential Guide for Network Administrators
If you’re a network engineer, chances are you will be responsible for choosing, implementing and operating some type of NAT for your organization.
Choosing what type of NAT to implement and operate can seem like a difficult decision. After all there are several different types of NAT that cater to unique networking requirements.
It is best to learn about all the different types of NAT before settling with one option. It is also necessary to consider all the benefits and drawbacks of different NAT types. This will enable you to choose the best option for your organization.
We shall cover not only the most common types for NAT but also their benefits and drawbacks. As a bonus point, we’ll also look at the common applications of each NAT type. This will help you acquire a thorough understanding of NAT.
Let’s begin now, shall we?
Common Types of Network Address Translation (NAT)
While there are several different types of NAT, the most commonly used types are as below. We shall also learn about the benefits and drawbacks of each type.
Static NAT
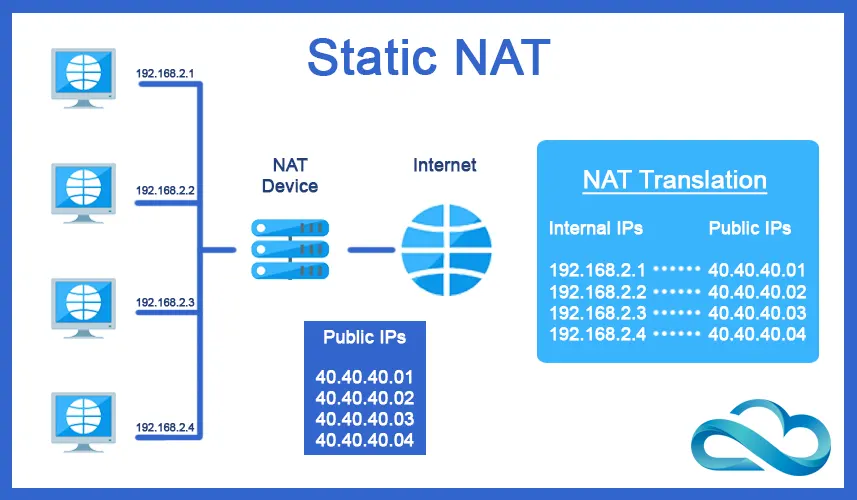
It maps a public IP address to a private IP address one-to-one. This type of NAT is used when a device on the internal network needs to be accessible from the internet using a static, public IP address.
Examples of devices that might use static NAT include:
Web servers: If a web server is located on a private network, it can use static NAT to make its content accessible to the internet.
Mail servers: A mail server located on a private network can use static NAT to receive email from the internet.
Remote access servers: A remote access server on a private network can use static NAT to allow remote users to access the private network using a static IP.
VoIP servers: A Voice over IP (VoIP) server on a private network can use static NAT to allow users to make and receive voice calls over the internet.
In these cases, the public IP address assigned to the device is statically mapped to its private IP address. This allows the device to be reached from the internet using a known and static IP address.
Benefits of Static NAT
- Provides a static, public IP address for a device on the internal network, which makes it easier to access the device from the internet.
- Provides a higher level of security as only the specific device is accessible from the internet.
Drawbacks of Static NAT
- Uses a public IP address that is permanently assigned to a single device. This limits the number of IPv4 addresses available publicly.
- Does not support many-to-one IP address mapping. This can be a limitation in environments where multiple devices need to share a single public IP address.
Dynamic NAT
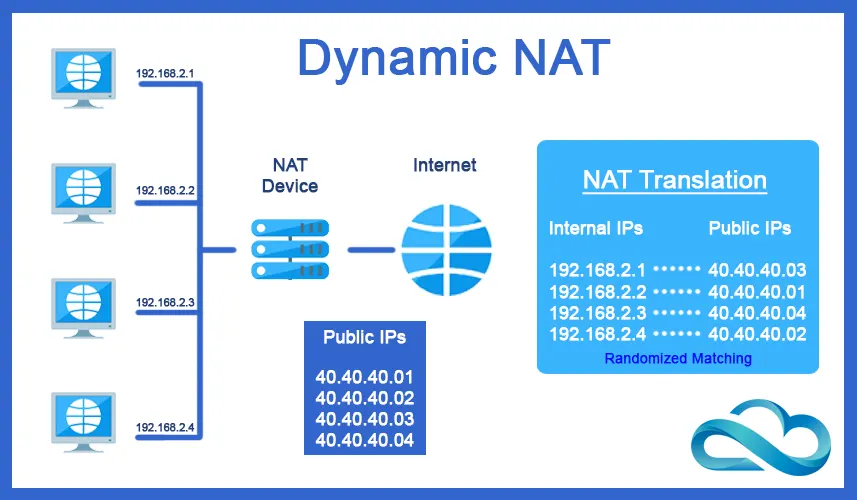
It maps a private IP address to a public IP address dynamically, using a pool of available public IP addresses. This type of NAT is used when multiple devices on the internal network need to access the internet using a single public IP address.
Examples of devices that might use dynamic NAT include:
Home networks: Many home networks use dynamic NAT to allow multiple devices, such as computers, smartphones, and gaming consoles, to access the internet using a single public IP address.
Small and medium-sized businesses: Small and medium-sized businesses often use dynamic NAT to allow multiple devices on their private network to access the internet, while conserving public IP addresses.
Remote workers: Dynamic NAT can be used to allow remote workers to access the internet using a public IP address assigned from a pool of available addresses, without requiring a static public IP address for each worker.
In these cases, the router or firewall performs dynamic NAT. It maps the private IP addresses of devices on the private network to available public IP addresses from a pool of available addresses.
This allows multiple devices on the private network to access the internet using a limited number of public IP addresses.
Benefits of Dynamic NAT
- Provides a pool of public IP addresses that can be used by multiple devices on the internal network.
- Automatically maps private IP addresses to public IP addresses, which makes it easier to manage the network.
Drawbacks of Dynamic NAT
- May result in IP address conflicts if multiple devices are assigned the same public IP address.
- Does not provide a static, public IP address for a device, which can make it more difficult to access the device from the internet.
Port Address Translation (PAT)
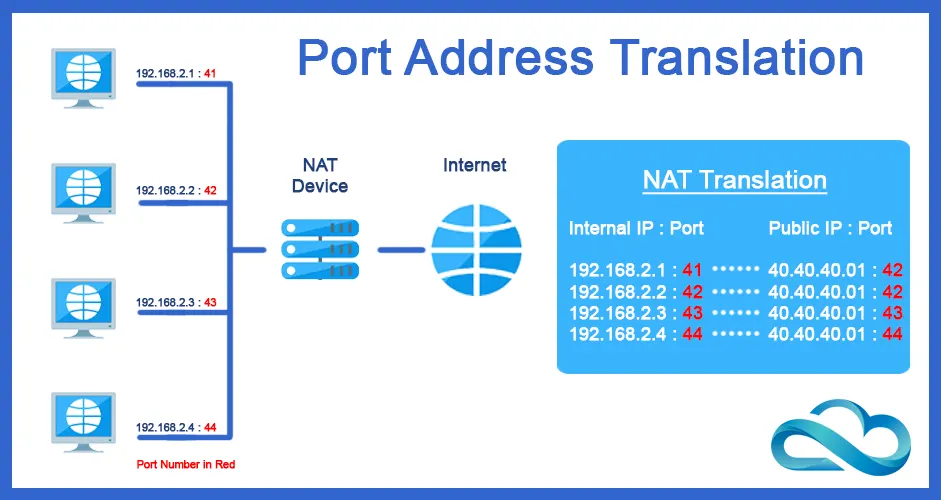
Also known as NAT Overload, PAT maps multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address using different port numbers.
This type of NAT is commonly used to allow multiple devices on the internal network to access the internet using a single public IP address.
Some unique and specialized applications of PAT are:
Overcoming Network Address Translation (NAT) Traversal issues: PAT can be used to overcome NAT Traversal issues in real-time communication applications such as voice and video calls, where private IP addresses are hidden behind a public IP address.
Content Delivery Networks (CDN): PAT can be used in CDN deployments to manage traffic and distribute incoming requests across multiple servers, improving network performance and reliability.
Disaster Recovery: PAT can be used in disaster recovery scenarios to provide remote access to resources on a secondary network, allowing remote workers to continue their work even in the event of a network failure.
Internet of Things (IoT) Deployments: PAT can be used in IoT deployments to provide internet access for IoT devices on a private network, without requiring a dedicated public IP address for each device.
Network Address Translation Load Balancing: PAT can be used in load balancing scenarios to distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers, improving network performance and reliability.
These unique and specialized applications demonstrated its versatility and flexibility as a networking solution. This allows it to be used in a wide range of networking scenarios to overcome challenges and improve network performance.
Benefits of PAT
- Supports many-to-one IP address mapping, which allows multiple devices on the internal network to share a single public IP address.
- Conserves public IP addresses, as only a single public IP address is needed for multiple devices.
Drawbacks of PAT
- Can result in reduced performance due to the use of multiple port numbers to map multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address.
- Does not provide a static, public IP address for a device, which can make it more difficult to access the device from the internet.
Overlapping NAT
It is used when two different private IP address ranges are used on two different internal networks, and both networks need to access the internet. This type of NAT is used to translate between the two private IP address ranges to the public IP address range.
The most common use cases for Overlapping Network Address Translation (NAT) include:
Test and Development Environments: Overlapping NAT can be used to provide isolated network environments for testing and development. This allows multiple teams to work independently on the same network without interfering with each other.
Remote Access: Overlapping NAT can be used to provide remote access to resources on a private network. This can allow remote workers to access internal resources using a VPN connection.
Virtual Private Network (VPN) Connections: Overlapping NAT can be used to resolve conflicts between the private IP address ranges used by a VPN connection and the private IP address ranges used within an organization's network.
Cloud Computing Environments: Overlapping NAT can be used to resolve conflicts between the private IP address ranges used by multiple tenants in a cloud computing environment. This allows them to access resources on their virtual networks.
Multi-Site Deployments: When multiple locations use the same private IP address ranges, it may lead to conflicting IP addresses and network connectivity issues. Overlapping NAT can be used to resolve this in multi-site deployments.
These are some of the most common use cases for overlapping NAT, where it is used to resolve conflicting IP addresses and network connectivity issues, improving network performance and reliability.
Benefits of Overlapping NAT
- Supports the use of different private IP address ranges on multiple internal networks.
- Allows devices on different internal networks to access the internet.
Drawbacks of Overlapping NAT
- Can be complex to set up and maintain. It requires mapping between multiple private IP address ranges to a single public IP address range.
- Does not provide a static, public IP address for a device. This can make it more difficult to access the device from the internet.
Bi-directional NAT
It maps a private IP address to a public IP address, and maps a public IP address to a private IP address. This type of NAT is used when a device on the internal network needs to access a device on another internal network using a public IP address.
Some specialized use cases of Bi-directional NAT are as follows:
Connecting Disparate Networks: Bidirectional NAT can be used to connect disparate networks that use conflicting IP address ranges, allowing them to communicate with each other.
Network Address Translation Over VPN: Bidirectional NAT can be used to perform NAT functions over a VPN connection. This provides a secure and efficient way to connect remote networks.
Virtual Machine Mobility: Bidirectional NAT can be used to support virtual machine mobility. This allows virtual machines to move between different physical hosts and maintain network connectivity.
Network Segmentation: Bidirectional NAT can be used to segment networks. This provides a secure and efficient way to separate different types of network traffic and restrict access to resources.
Benefits of Bi-directional NAT
- Supports both one-to-one and many-to-one IP address mapping.
- Allows a device on one internal network to access a device on another internal network using a public IP address.
Drawbacks of Bi-directional NAT
- Can be complex to set up and maintain, as it requires mapping between both private and public IP addresses.
- Does not provide a static, public IP address for a device, which can make it more difficult to access the device from the internet.
Conclusion
NAT is a crucial component of modern computer networking architecture. It can be implemented in several different ways with each way being unique.
Different types of NAT cater to certain unique requirements. When it comes to choosing a suitable NAT type, you should know what your core requirements are.
Once you know your core requirements, picking a NAT type becomes easy. I hope the use cases for each NAT type presented in this article helped you further your knowledge of NAT and computer Networking.
What more would you like to learn?
























































































































