SIP 101 - The Best Guide of 2022
The Internet is a very big place and enables users to do many wonderful things. But the internet is also chaotic. It's like having everyone in the world in the same place at the same time.
Now, the internet lets you communicate with anyone you’d like. There’s one catch, how do you communicate with a particular person in this ocean of internet users?
You could scream someone’s name out, digitally of course, but there would be so many people with the same name on the internet.
Internet communication seems like a tricky task now, doesn’t it?
Thanks to signaling, it's not! Signaling allows internet users to communicate with particular people via text, voice and video.
The signaling protocol that forms the backbone of Internet communication and enables all of this is the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP).
Let’s understand and learn everything about it, shall we?
What is the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)?
Going by the standard definition, Session Initiation Protocol is a signaling protocol developed by Internet Engineering Task Force for initiating, maintaining, modifying and terminating real-time communications sessions between IP devices.
Text, voice and video and other forms of communication are made possible between two or more IP-enabled devices using SIP.
SIP is widely used in IP telephony, private IP-based communication systems as well as mobile phone calling over Voice over LTE (VoLTE).
SIP is a text-based protocol and many of its elements are based on two more protocols viz. Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
So, it follows the same request/response model of HTTP. Being a text-based protocol means that SIP messages are not only easy to read but also easy to debug.
Similar to email headers in SMTP, SIP messages contain all the required metadata to establish a communication session between two users.
With that, you know what a Session Initiation Protocol is. We can not head on and check all its important features.
SIP Features
- SIP is a signaling protocol and resides in the application layer. It is only used to initiate, modify, manage and terminate communication sessions.
- Being in the application layer, SIP is independent of the underlying network transport protocol. Network engineers can choose from TCP, UDP, TLS and other NTPs for SIP.
- The media details are handled by the Session Description Protocol. The bidirectional exchange of text, voice and video data is handled by the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP).
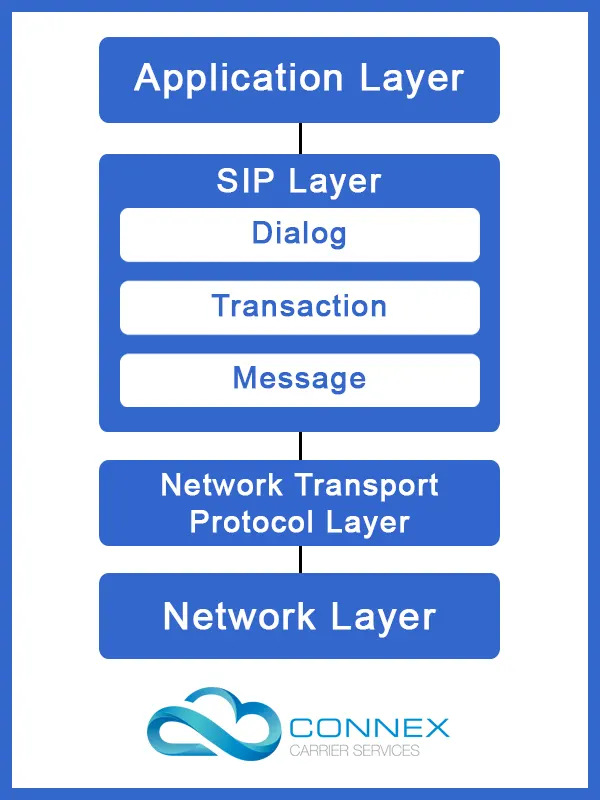
- SIP sessions include Internet Telephony, VoIP, Video Conferencing, or other different forms of unified communication.
- SIP is secure and supports end-to-end and hop-to-hop authentication. End-to-end encryption is also possible with SIP with an added penalty in the form of latency.
- Users in a SIP session can communicate using unicast, multicast, broadcast or a combination of these methods.
Now you know the basics and features of the Session Initiation Protocol. Next, we will learn about the Network Elements that make use of SIP for communication.
Network Elements
Something as simple as calling requires a few key players to enable the communication. Let us learn who these players are and what role they play.
User Agent
A User Agent is a network endpoint that sends, receives SIP requests and manages SIP sessions. User agents are the client and server components in the network.
The user agent that sends SIP requests is known as the User Agent Client (UAC) and the one receiving and responding to SIP messages is known as the User Agent Server (UAS).
In other protocols such as HTTP, the role of each UA is fixed as either the client or server. In SIP, a UA can play both roles. The roles are specified and played accordingly only for the duration of that particular SIP session.
Proxy Server
While any two SIP devices can directly communicate with one another, they need an intermediary. This intermediary handles the SIP request, finds its designated recipient, routes the call via the best route and connects the two SIP devices.
A proxy SIP server interprets the SIP message and rewrites its section if necessary before forwarding it to its destination or the nearest proxy server to the destination.
SIP proxy servers are also useful for enforcing telecommunication policies, ensuring the authenticity of the call and determining whether a user is authorized to make the call and use the specific caller ID.
Registrar
A Registrar is a SIP Network Component that accepts REGISTER requests from SIP User Agents. It also records their IP address and other parameters and stores them on an Address on Record (AoR).
When a UAC sends out a SIP request for a UAS, the registrar checks the AoR and forwards the SIP request to the latest registered IP of the particular UAS/SIP endpoint.
The Registrar also manages the expiry for IP addresses. Each UA is allotted a specific time after which their entry in the AoR expires. The UA is required to send a new REGISTER request and continue the cycle.
Session Border Controller
As the name implies, a Session Border Controller (SBC) is a special purpose device that is deployed at the network borders. An SBC protects and regulates the flow of IP-based communication sessions.
Along with maintaining a full session state, an SBC can also undertake the following functions:
Security - Ensuring secure signaling through TLS, IPSec, etc. and secure media transfer using SRTP.
Connectivity - Ensuring seamless connectivity through different parts and components of telephony and IP-based networks.
An SBC achieves this by using NAT traversal, SIP normalization, VPN connectivity, IPv4 to IPv6 networking and many other get-arounds.
Quality of Service - an SBC is usually responsible for implementing and enforcing network policy and traffic prioritization.
This is done by Rate limiting, resource allocation, call admission control, traffic policing and other similar measures/frameworks.
Gateway
A SIP gateway is an interconnect that enables telecom networks using different technologies and protocols to connect with one another.
The telecom sector is not homogeneous in terms of the technology, protocols and communication methods used.
A SIP Gateway allows a user on a VoIP network to easily connect with a user on the analog legacy telephony system or the PSTN.
We only have one part to cover in this article now. So let's head on and learn how SIP works!
How Does SIP Work?
To properly understand how SIP works to connect a call, we will follow the entire process step-wise.
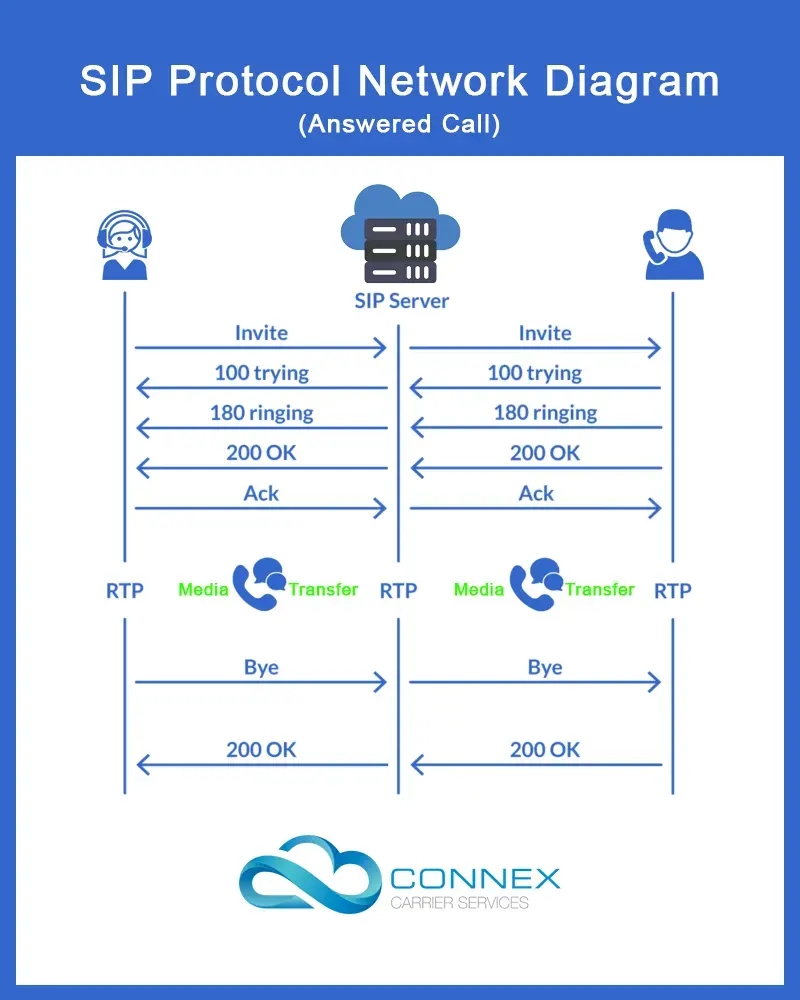
Step 1 - Sending an Invite
The caller dials a number or places a VoIP call through an App. The App sends the necessary information in the form of a SIP packet to a SIP server.
The SIP server then sends the invitation to the designated recipient. The SIP server informs the caller with a 100 Trying SIP message that it is trying to connect the call.
Step 2 - Connecting
Once the connection request is received by the call recipient, it responds with a 180 Ringing SIP message to the SIP server and rings the phone/device.
The SIP server informs the caller with the same 180 Ringing message and the ringing tone is played at the caller’s end.
Step 3 - Accepted Call
Once the call recipient notices the device ringing and answers the call, the device sends a 200 OK SIP message to the SIP server. The SIP server relays the 200 OK SIP message to the caller.
The caller device sends an ACK SIP message to the SIP server which is relayed by it to the call recipient. Once the ACK SIP message is received, the connection has been established.
Step 4 - Media Transfer
Once the connection has been established, media exchange begins via RTP. SIP is not involved in this step. The media transfer can be a voice, video, text or a combination of the three or some other format of media too.
Step 5 - Termination
Once the caller and call recipient are done talking, either party can terminate the connection by pressing disconnect on their device.
Once the disconnect button is pressed, the device sends a BYE SIP message to the SIP server. The SIP server relays the same to the other party.
The other party responds with an ACK SIP message which is relayed to the first party by the SIP server and thus the connection is terminated.
Other Possibilities
This is how SIP works for a call that connects. For other instances when a call recipient is busy or doesn’t answer, the first two steps remain unchanged.
In case the call recipient doesn’t respond, his device responds with a 486 BUSY SIP message and the SIP server relays it to the caller.
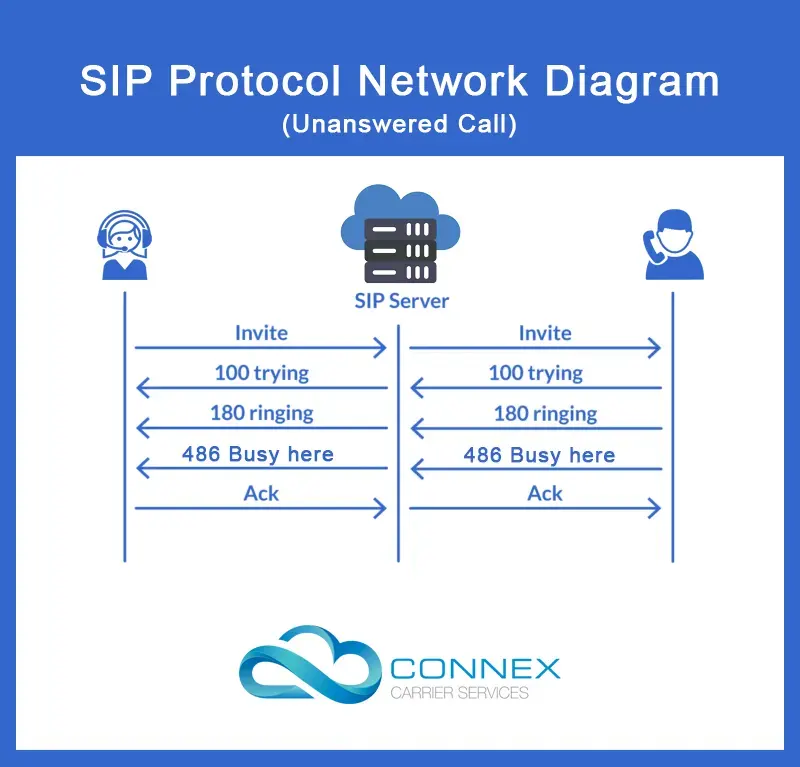
The caller device responds with an ACK SIP message and informs the caller that the call recipient is busy.
In case the call recipient declines the call, his device responds with a 603 Decline SIP message and the SIP server relays the same to the caller.
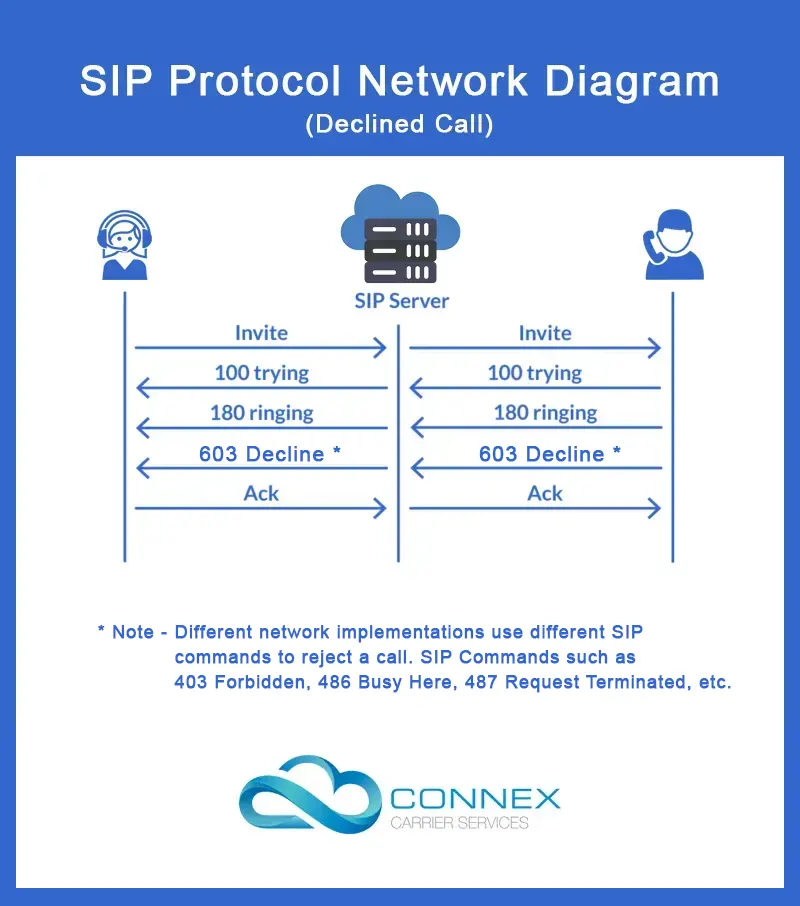
The caller device responds with an ACK SIP message and informs the caller that the call recipient has declined the call.
Wrapping Up
Session Initiation Protocol is important for not only VoIP communication but also for other forms of communication.
SIP being simple and text-based make it the top choice for establishing communication over IP. With the knowledge you’ve gained through this article, you will be able to understand the ins and out of IP-based communication.
Learning about how technologies that drive our daily lives is helpful in many ways. We hope this article covered everything you wanted to learn about SIP.
























































































































