False Answer Supervision Detection - The Ultimate Tool for Preventing VoIP Fraud
When it comes to innovation and ingenuity, scammers are always present at the leading edges of technology. Every new technology brings more improvements and opportunities; for the scammers as well.
VoIp technology revolutionized global communication and along with it the scope of scams. Among VoIP scams, one that stands out the most along with spoofing is False Answer Supervision scams.
FAS is a type of VoIP fraud where fraudsters make it appear as though a call was answered, when in fact, it was not. As a result, a user ends up paying for a call conversation that did not happen.
Thankfully, there is a safeguard to protect against such scams, it's known as False Answer Supervision Detection. We will explore FAS detection in more detail in this blog.
How the scam works, how FAS detection prevents it and what risks are involved when not implementing FAS detection will all be covered in great detail.
So let’s start with some basics then, shall we?
What are False Answer Supervision Scams?
False answer supervision scams in VoIP refer to a type of fraud where fraudsters manipulate call data to make it seem like a call was answered when it was not.
This can occur when a user makes a call, but instead of ringing, it goes straight to voicemail or is terminated before it can be answered.
The fraudster then uses this call data to charge the user for a completed call, even though no conversation actually took place.
For example, imagine you made a call to your friend, but their phone was turned off, and the call went straight to voicemail.
In a false answer supervision scam, the fraudster could manipulate the call data to make it seem like the call was answered and a conversation took place. They would then charge you for the completed call, even though no actual conversation occurred.
False answer supervision scams can result in significant financial losses for both carriers and customers, as fraudulent charges can quickly add up.
To prevent false answer supervision scams, carriers can implement False Answer Supervision Detection, a fraud prevention mechanism that helps detect and prevent false answer fraud.
Let’s learn what FAS Detection is!
What is False Answer Supervision Detection (FAS Detection)?
False Answer Supervision (FAS) Detection is a feature in VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) and telecom systems that helps detect and prevent fraudulent activity related to billing and call termination.
In telecom systems, FAS detection involves monitoring for false answer signals that indicate a call has been connected to a destination but has not actually.
This can happen if the call is terminated to an automated answering system or if the call is dropped before a person can answer. In these cases, the caller may be charged for a full call even though it was not completed.
To prevent this type of fraud, telecom systems use FAS detection to detect these false signals and prevent the call from being billed or to adjust the billing accordingly.
In VoIP systems, FAS detection can also help detect and prevent other types of fraud such as call spoofing and call hijacking.
Before we find out how FAS detection works, let’s understand how a False Answer Supervision Scam is committed in VoIP!
How is a False Answer Supervision Scam committed in VoIP?
To prevent something from happening, it is important to understand the process that makes it possible in the first place. Here's a detailed explanation of how a false answer supervision scam is committed in VoIP.
Step 1 - The Scammer sets up a VoIP gateway
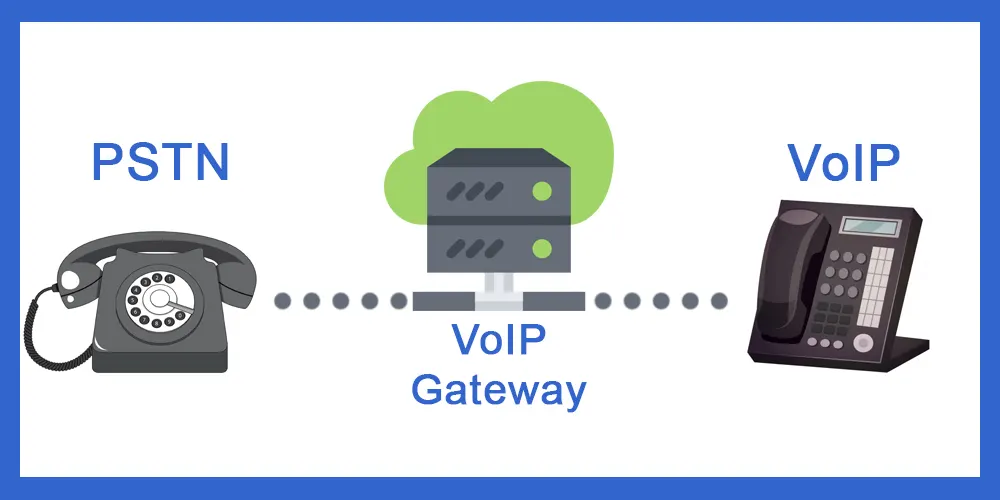
The first step in the scam is for the scammer to set up a VoIP gateway. This is a device that connects the VoIP system to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
The gateway is configured to generate a false answer signal when a call is terminated to a specific destination number.
Step 2- The Scammer identifies Vulnerable Routes

Once the gateway is set up, the scammer will identify vulnerable routes that can be exploited. These are typically routes that have low quality or low cost termination points. The scammer will terminate calls to these routes and generate a false answer signal.
Step 3 - The False Answer Signal is Generated

When a call is terminated to a vulnerable route, the VoIP gateway generates a false answer signal that makes it appear as if the call has been answered by a human.
This signal can be generated in a number of ways, such as by playing a pre-recorded message or by using a tone generator.
Step 4 - The Caller is Billed for a Full Call

When the false answer signal is generated, the VoIP system believes that the call has been completed and the caller is billed for a full call.
This can happen even if the call was not actually answered by a human or if it was only connected to an automated system.
Step 5 - The Scammer Profits

The scammer profits from the scam by receiving a portion of the revenue generated by the billing. In some cases, the scammer may also sell access to the vulnerable routes to other fraudsters.
Now that you know how False Answer Supervision Scams work, let’s find out how False Answer Supervision Detection prevents such scams!
How does FAS Detection Prevent False Answer Supervision Frauds?
FAS Detection works by detecting and flagging calls that generate false answer signals, allowing service providers to take appropriate action to prevent fraud.
The process of how FAS Detection works to prevent false answer fraud can be explained in the following steps:
Step 1 - Detection of False Answer Signals

FAS detection detects false answer signals by analyzing the signaling information exchanged between the originating and terminating endpoints.
False answer signals occur when a call is initiated but not answered, resulting in a brief ringing tone or silence. The FAS detection system analyzes the signaling information to determine whether a false answer signal was generated.
Step 2 - Flagging of Suspicious Calls

If a false answer signal is detected, the call is flagged as suspicious by the FAS detection system. This alerts service providers to the possibility of fraudulent activity and allows them to take appropriate action to prevent further damage.
Step 3 - Verification of Suspicious Calls

Once a call is flagged as suspicious, the FAS detection system verifies the call by sending a query to the terminating endpoint to determine whether the call was answered or not.
If the terminating endpoint confirms that the call was not answered, the call is confirmed as fraudulent and further action can be taken to prevent further damage.
Step 4 - Call Blocking or Diversion

Depending on the level of risk associated with the fraudulent call, service providers may take different actions to prevent further damage.
If the call is confirmed as fraudulent, service providers may block the call entirely, preventing the call from being completed.
Alternatively, they may divert the call to a special destination, such as a voicemail system or an automated fraud detection system, to prevent further damage.
Step 5 - Real-time Monitoring

FAS detection operates in real-time, continuously monitoring calls for false answer signals and suspicious activity. This allows service providers to detect and prevent fraudulent activity as soon as it occurs.
Thus minimizing the potential for financial losses and reputation damage.
The effectiveness of FAS detection in preventing false answer frauds depends on several factors.
The quality of the signaling information, the accuracy of the detection algorithm, and the speed of the verification and blocking/diversion processes are prime among these.
Additionally, FAS detection is just one part of a comprehensive fraud prevention strategy that should include other measures such as STIR/SHAKEN, call pattern recognition, and Robocall Mitigation.
But what if you don’t implement FAS Detection? What happens then? Well, let’s find out!
What are the Top 7 Risks of Not Implementing FAS Detection?
The short answer is that a lot can go wrong if you opt for not implementing False Answer Supervision Detection. To make the proposition of implementing FAS Detection more convincing, here are 7 risks involved in not implementing FAS Detection:
1. Financial Losses

FAS fraud and other types of VoIP fraud can result in loss of revenue for the carrier. Fraudulent activity can result in charges for services that were never provided or that were provided at a lower cost than the charge.
There are many ways in which this can happen. There are billing frauds, premium calling rate number frauds and more that help accomplish this. All of it can result in reduced revenue for the carrier and financial losses.
In cases where customers are affected by fraudulent activity, carriers may be required to provide refunds or compensation. This can further erode the profits of a carrier, particularly if a large number of customers are affected.
2. Call Hijacking
Scammers can use FAS to hijack ongoing calls and gain access to sensitive information or resources. Call hijacking involves taking control of an ongoing call by intercepting the signaling and media streams.
This may also result in data/information privacy breach. Moreover, scammers can also access sensitive information such as credit card numbers, back details, password credentials, etc.
3. Loss of Customer Trust
Trust between a VoIP provider and their customers is an important factor for the profitability and secure future for businesses in this industry.
Failure to implement FAS Detection can result in a loss of customer trust. The customers may view carriers that do not implement adequate fraud prevention measures as unreliable and insecure.
This can further add to loss of revenue and result in reduced customer loyalty, increasing the rate of churn.
4. Reputation damage

While some say negative publicity is still good for you, such is not the case when it arises from compromised consumer safety. Negative news not only travels fast on the internet but has long lasting effects in a rather dynamic age of the internet.
Fraudulent activity can damage the reputation of businesses and service providers. As mentioned earlier, trust is an important cornerstone of the business world. When this trust is lost it gets further difficult to gain new customers and retain the existing.
Thus, when a brand is associated with lack of safety for consumers, they’re bound to bleed revenue and market share to their competition.
5. Legal Liability

Organizations that do not implement adequate fraud prevention measures, including FAS Detection, may be held legally liable for damages resulting from fraudulent activity.
In some cases, failure to implement FAS Detection can result in criminal liability. FAS fraud is a criminal offense. The service providers may be held liable if they knowingly fail to implement measures to prevent fraudulent activity. This can result in fines, imprisonment, and other criminal penalties.
Failing to implement FAS detection can also result in a violation of consumer protection laws. Consumers have the right to expect secure and reliable service.
Failure to implement adequate fraud prevention measures can result in a breach of this expectation.
6. Regulatory Action due to Non-Compliance

There are many regulatory authorities around the world that require carriers, VoIP providers and telecom operators to implement FAS Detection and other safeguards.
Failure to implement FAS Detection can result in regulatory non-compliance, which can lead to regulatory fines and penalties. In some severe instances of repeat offenses, it may also lead to the revocation of licenses to operate for the carrier or provider.
Carriers that fail to comply with industry regulations and standards may also face restrictions on their business activities. These carriers may be excluded from databases or other services that ensure customer safety.
This can lead to further losses in terms of revenue and market share.
7. Competitive Disadvantage
Consider all the negatives associated with not implementing FAS detection. There is financial loss, call hijacking, loss of customer trust, legal liabilities and other things.
If a carrier or provider is plagued with such problems, how is he supposed to remain competitive in the market? Businesses, especially in the VoIP industry face fierce competition as technology here changes at an even faster rate than other industries.
Carrying around even one of the above mentioned negatives will severely impact a provider’s or carrier’s ability to remain competitive in the market.
Concluding
FAS scams are ingenious but thankfully we have an effective safeguard in the form of FAS Detection. Now you know how the scams work and how FAS Detection prevents it.
We’re sure you’ll do your best to safeguard not just yourself but your customer using FAS Detection.
Discussing the risks involved made it clear as to how sharply the benefits of implementing FAS outweigh other factors.
























































































































