WebRTC 101 - The Best Guide for Beginners

There has been a surge in the need for voice and video communication. As the world was forced indoors due to the pandemic, a lot of people had to work from their homes.
At the same time, as people couldn’t socialize, the only option they had left was video and voice calls. This further added to the rise in demand for video and voice calls.
The legacy telecom systems fall short of delivering a convenient, connected and immersive experience . It was thanks to the internet and WebRTC that the world managed to stay connected and social through a global pandemic.
The internet hails WebRTC as the next frontier in digital communication. But what is WebRTC and how does it work?
We’re going to answer these questions and a lot more in this article. Let's begin then, shall we?
What is WebRTC?
WebRTC is an open-source project that allows web browsers and mobile applications to communicate with one another in real time.
With WebRTC voice and video communications can work inside a webpage via direct peer-to-peer communication. This eliminates the need for installing plugins and or downloading native applications.
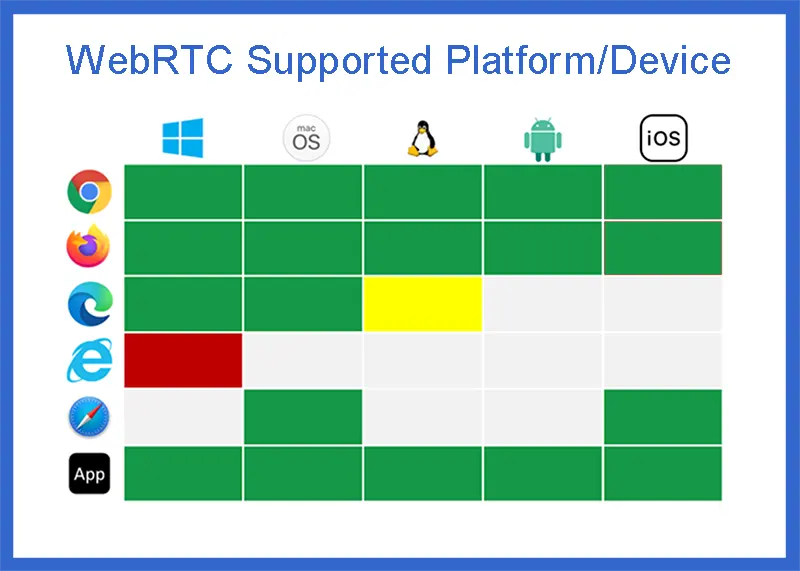
According to the project, their main objectives are as follows:
- Enable the development of RTC applications for browsers, mobile platforms and IoT devices.
- Provide a rich and high-quality communication experience to the users.
- Standardize all RTC communications under a set of common protocols.
On a technical front, WebRTC is an HTML5 JavaScript specification that comes along with a set of web APIs. Combined with the communication protocols, it enables uninterrupted, bidirectional audio and video communication between web browsers.
STUN/TURN servers, JSEP, ICE, SIP, NAT, UDP/TCP, network sockets and more are among the network protocols WebRTC uses.
In terms of applications, WebRTC can be used for click-to-call, peer-to-peer streaming, instant messaging, video conferencing and other audio/video communications.
Now you know what WebRTC is. Let's move ahead and understand how WebRTC works!
How does WebRTC work?
WebRTC has three primary components and each plays an important role in enabling bidirectional voice and video communication.
Let us check these components and see how each one works.
Peer Connection
The primary component of WebRTC is the Peer Connection. This is the component that allows browsers to find each other and establish a direct connection between the two.
As the connection is directly established between the two peers, there is no need for an intermediary service to connect the two.
Once connected, peers can transmit and consume voice, video and other data.
Media Stream
Media Stream is the API that allows a browser or a mobile app to access the device’s camera and microphone.
It monitors and controls all the information of the device concerning the capture and rendering of the media. In most instances, it controls the audio and video data streams but can also control other forms of data streams.
Data Channel
A bidirectional data channel needs to be established after the primary connection has been made. Once this is done, the transmission of media can begin between peers.
WebRTC data channels work on Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP).
We can now move on and understand the entire process step-by-step.
Steps Involved in Establishing Communication via WebRTC
WebRTC is a collection of different technologies and protocols that enable P2P communication. These steps need to happen in a given sequence.
Let’s dig right into it!
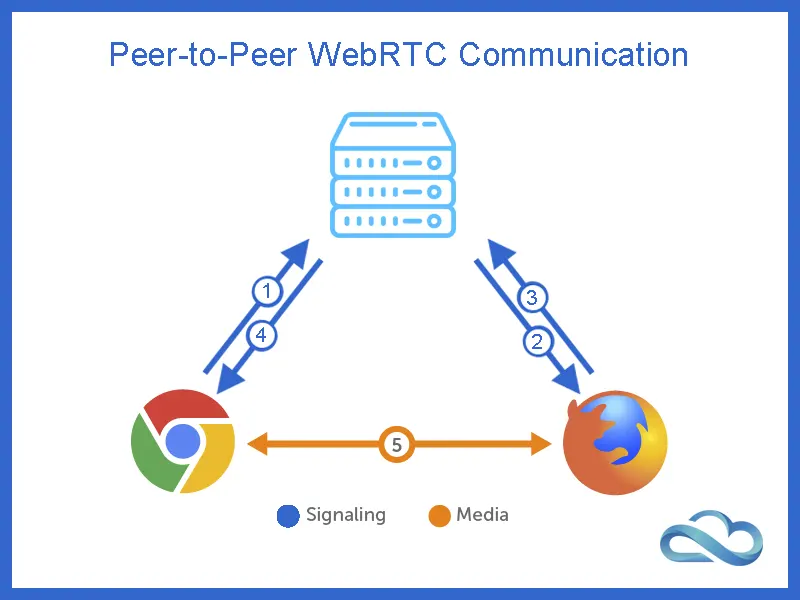
Step 1 - Signaling
Before you can begin exchanging media, you need to establish a connection with your peer. For that you need Signaling.
Signaling involves initiating and managing a communication session. The peer initiating the communication session can use any protocol, but in open-source telecoms, the prefered protocol is SIP, which encapsulates the SDP describing the audio..
The initial packet sent by the peer contains a plethora of information including the following.
- IP addresses of both peers.
- Complete session description
- Media description
- Data channel description
Signaling allows peers to set up and manage a coordinated bidirectional communication session. Signaling is not a part of WebRTC. Thus, developers can opt for different network protocols for Signaling.
Step 2 - Connecting
Signaling is followed by connecting. Connecting is the process of securing a bidirectional line of communication between peers.
WebRTC communications are P2P and could only use a server for coordination, however in business telecoms it makes more sense to proxy via a server.
In some instances, the two peers can be using different Internet Protocols. In such cases, establishing a direct line of communication becomes difficult as having different NAT firewalls prevents RTC.
WebRTC makes use of the Interactivity Connectivity Establishment (ICE) protocol to combat this. ICE servers find the best and the most direct way two peers can directly communicate with one another. (ICE can be used just by SIP as well)
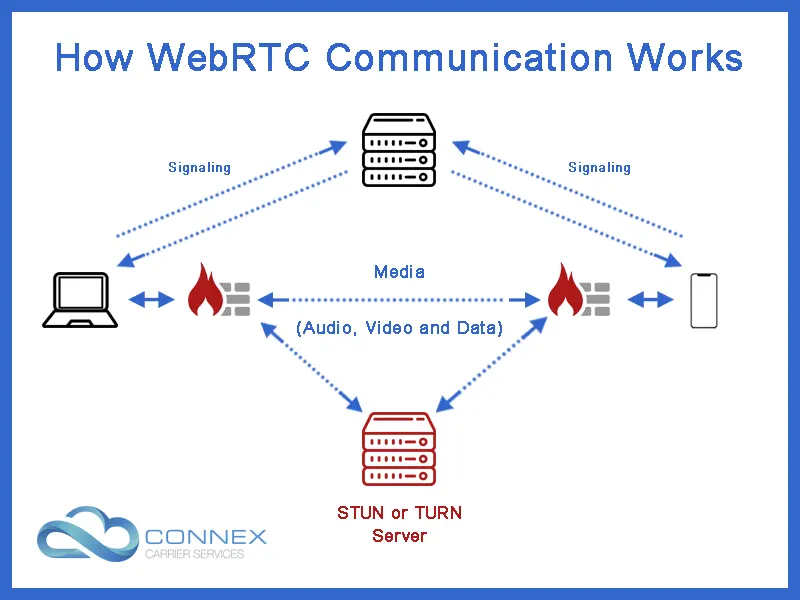
However, in some cases, ICE servers are unable to find a route to enable P2P communication. In this case, WebRTC can make use of Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (STUN) servers.
A STUN server helps detect your public IP address. Which is important as sometimes your browser does not know this.
However, sometimes even STUN isn’t enough to enable P2P communication. This is most often the case where 2 devices are trying to connect, but they are both behind firewalls, or there is an active attempt to block communications..
In this case, P2P communication can still be established using Traversals Using Relays around NAT (TURN) servers. TURN servers act as traffic relays between the two peers. This enables them to communicate despite network restrictions.
Step 3 - Securing
WebRTC P2P connections are relatively more secure compared to other protocols due to security being implemented as standard. However, this alone doesn’t make them completely invulnerable.
WebRTC’s framework ensures all communication between the two peers is secured. Data and media remain encrypted and confidential at all times as they make their way from peer to peer even if a third party is involved.
WebRTC uses two protocols, SRTP and DTLS. These ensure that communications remain secure and malware-free.
Let’s learn about these protocols!
Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS)
Based on TLS, DTLS is a security protocol that secures datagram transport. Applications and services that are delay-sensitive, tunneling applications, etc. find DTLS to be the best solution for security.
DTLS requires both the peers and servers if any involved to agree upon certain values known as ciphers to secure communication.
Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP)
SRTP provided encryption, message authentication and integrity and replay attack protection to RTP data. SRTP secures the media streams between the two peers.
It encrypts the media streams using the same keys generated by DTLS. This protocol was specifically designed for encrypting RTP data packets.
Step 4 - Communication
Once all the preceding steps have been completed, bidirectional communication can begin between the peers. WebRTC allows users to add or remove media streams anytime during the duration of the communication session.
These media streams are bundled together with two core WebRTC protocols.
Real-Time Communication (RTC)
The RTC protocol is designed to carry real-time delivery of data and media streams such as voice and video.
Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP)
RTCP allows system or network administrators to monitor the quality of audio or video calls from the collected metadata. This protocol monitors packet losses, latency and other VoIP parameters of concern.
In terms of communication, WebRTC focuses on the following.
- Quality over latency.
- The authenticity of messages, media and data.
- Reduced bandwidth cost.
- Secured E2E Communication.
- Coordinating with SDP values and more.
Once the communication has ended, either of the peers can terminate the sessions. Then the direct line of communication will also be terminated immediately.
To Conclude With
Though WebRTC was introduced back in 2011, it wasn’t until recent few years that it became so prominent. The technology is solid and future-proof as it can prove to be pivotal in the transition to Web3.
Being a P2P and decentralized technology, it ticks all the requirements for being a mainstay in the Web3 world.
Moreover, as it is open source and free to use for personal and commercial applications, it may turn into the backbone of future decentralized communication.
























































































































